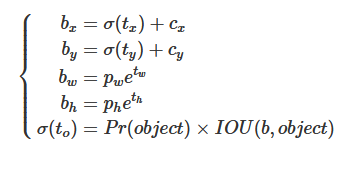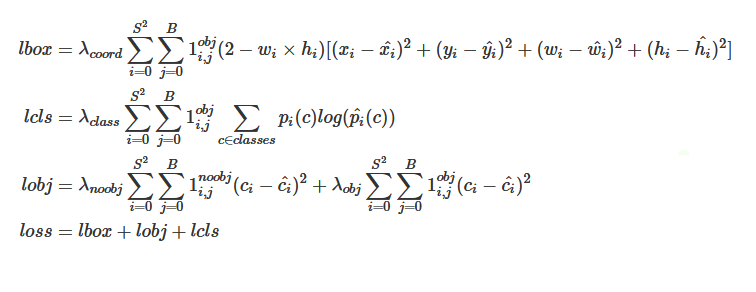Yolo v3 Principle Introduction
Yolo v3 Principle Introduction
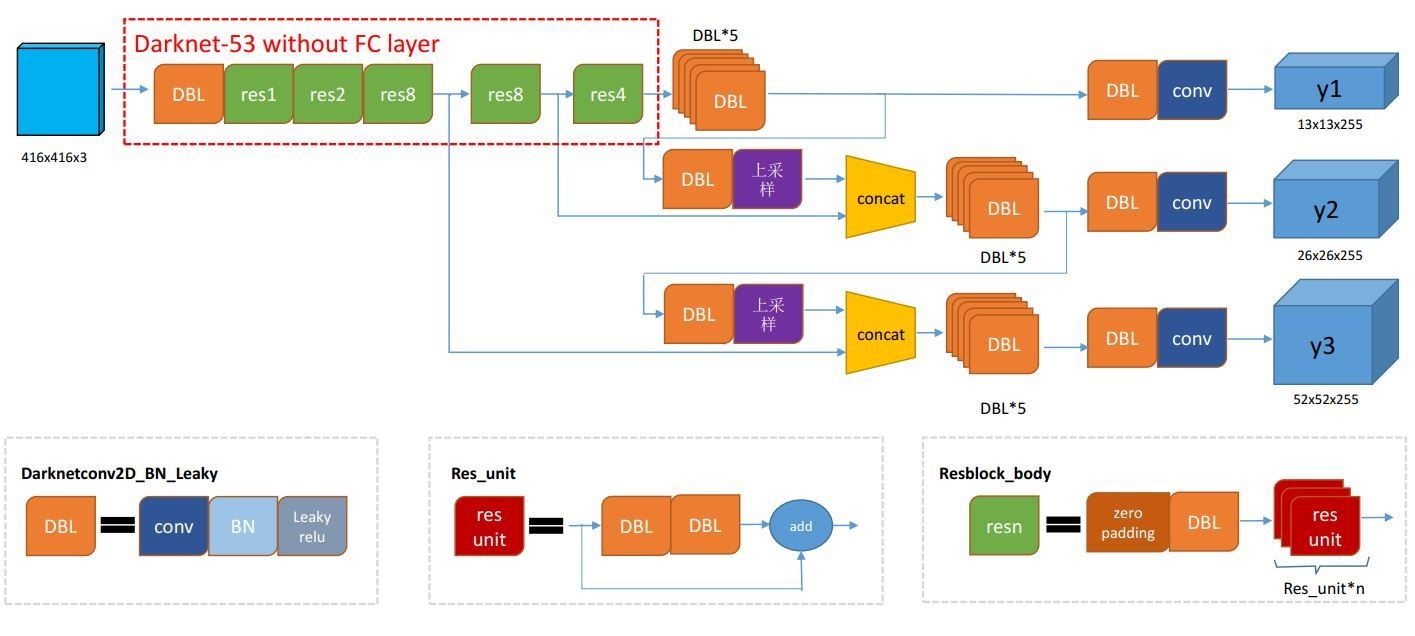
Yolo-v3
Model structure
Yolo v3 Model Structure Code Snippet
Shape of prediction and target
- prediction
- head1: torch.Size([bs, 3, S, S, 5+cls])
- head2: torch.Size([bs, 3, S, S, 5+cls])
- head3: torch.Size([bs, 3, S, S, 5+cls])
- S为(13, 26, 52)
- len(c, x, y, w, h) == 5
- c为置信度, 代表有样本的可能性, BCEWithLogitsLoss(c_p, c_t)
- 输出的cls为总类别数, CrossEntropyLoss(cls, label)
- target
- scale1: torch.Size([bs, 3, S, S, 6])
- scale2: torch.Size([bs, 3, S, S, 6])
- scale3: torch.Size([bs, 3, S, S, 6])
- len(c, x, y, w, h, label) == 6
- c为(-1,0,1), 分别代表(忽略样本, 负样本, 正样本)
Difference between all kinds of box
- ground truth
- 一个image可能有若干bbox, each bbox shape is [label, x, y, w, h]
- 这里的xywh不论是归一化的值还是原始值, 都是相对于image的size
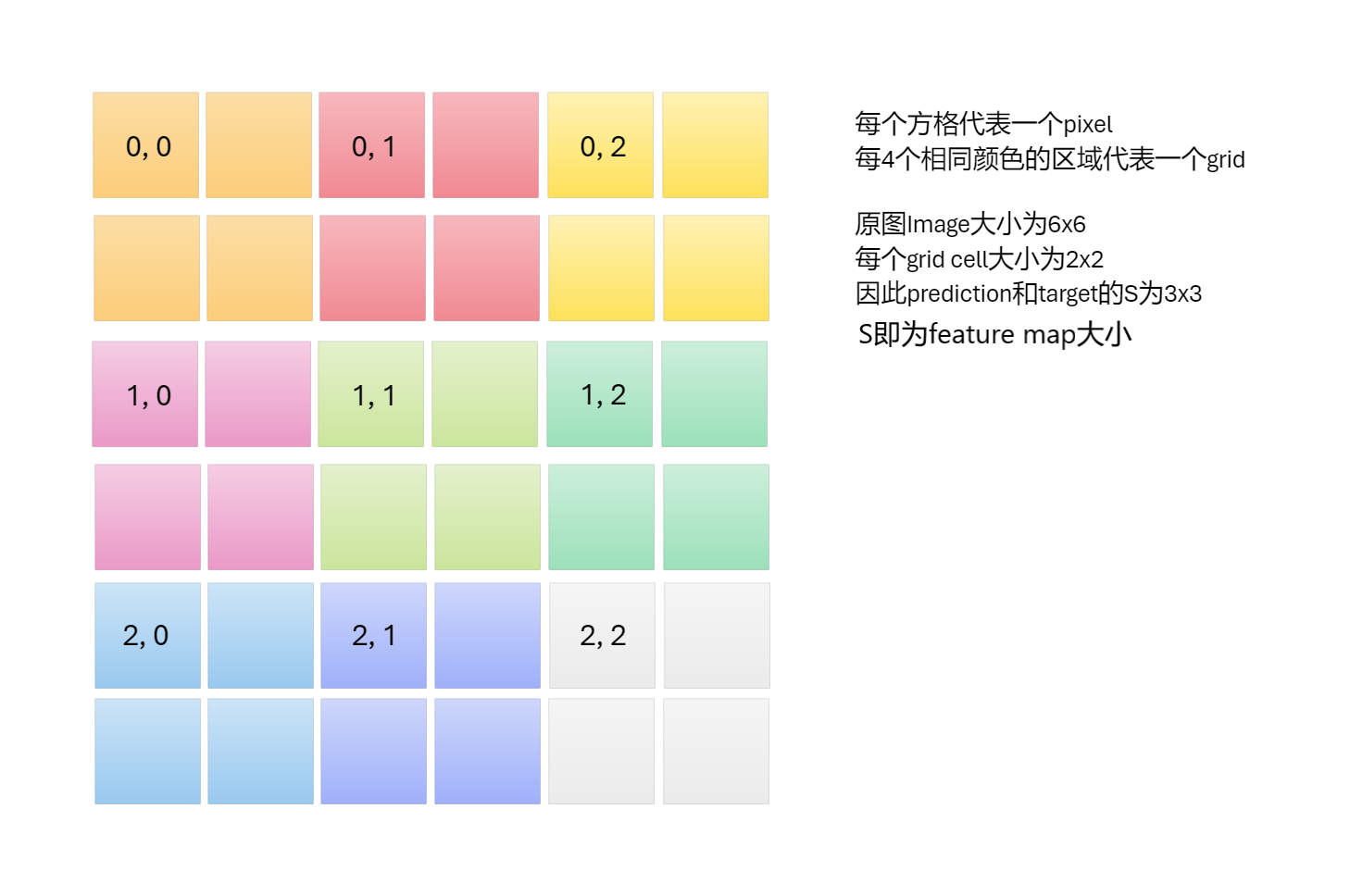
- grid cell
- 三种size的grid cell对应三个检测head
- size = [32, 16, 8] -> [IMAGE_SIZE//13, IMAGE_SIZE//26, IMAGE_SIZE//52]
- grid与image的对应
- anchor box
- 每个grid cell有三种不同scale的anchor, 有三种size的grid cell, 共有9种anchor
- anchor应该为(3, 2), 3种scale, len(w,h) == 2
- 每个anchor shape is [w, h], anchor只关心wh, 对ground truth shape的先验知识
- anchor的wh不论归一化与否, 都是相对于image的size
- prediction box (feature map)
Sample Types
- 正样本
- truth box与anchor计算iou后, 最大的iou对应的anchor, 与truth box关联, 记为正样本
- 负样本
- iou小于threshold的所有anchor
- 忽略样本
- iou大于threshold, 但不是正样本的其他anchor
Range of xywh values and How they mapping
Yolo v3 Dataset Code Snippet- ground truth -
preprocess-> target- 每一个ground truth bbox将与每种scale的一个anchor对应, 并用target记录
- 如果落在大的grid中必然也在小的grid中, 一共与三个anchor关联,
- 后续操作仅以一次关联示例
- 计算iou(bbox, anchor), 这里iou只关心wh, 将bbox和anchor的中心点叠到一起
- iou最大的标记为正样本
- target的一个scale就表示对应的anchor总数, anchor num == 3xSxS
- 3表示anchor scale, SxS表示grid的坐标i,j
- 关联的正样本在对应target中记录处理后的xywh
- truth bbox的w,h需归一化到SxS
- truth bbox的x,y需归一化到0-1, 归一化后是相对于一个grid内部
- x,y先归一化到SxS, 相当于feature map与image的映射
- grid的坐标i,j = 下取整(x, y)
- 归一化到相对于grid内部0-1, x, y = x-i, y-j
- target[:, :, i, j, xywh] = xywh, target[:, :, i, j, label] = bbox label
- 每一个ground truth bbox将与每种scale的一个anchor对应, 并用target记录
- prediction box (feature map)
- prediction[:, :, i, j, xywh]和target[:, :, i, j, xywh]是位置对应的
- 后续操作仅以任意某位置示例
- x_t, y_t是相对grid内部0-1的, x_p, y_p是随机值
- 将x_p, y_p做sigmod, 相当于把值域R映射到了值域0-1
- 优化目标就是sigmod(x_p, y_p)尽可能接近(x_t, y_t)
- w_p, h_p是随机值, w_t, h_t是理想中与关联anchor的wh接近的值, 范围在SxS
- w_t, h_t = (w_anchor x ratio_w, h_anchor x ratio_h)
- 优化目标是exp(w_p, h_p)尽可能接近(ratio_w, ratio_h)
- 等价于(w_p, h_p)尽可能接近log(ratio_w, ratio_h)
- 但ratio_w, ratio_h是未知的
- 等价于(w_p, h_p)尽可能接近log(ratio_w, ratio_h)
- 优化目标最终为exp(w_p, h_p) x (anchor wh)尽可能接近(w_t, h_t)
- (w_p, h_p)尽可能接近log((w_t, h_t) / (anchor wh))
- prediction[:, :, i, j, xywh]和target[:, :, i, j, xywh]是位置对应的
yolo-v3 loss function
Yolo v3 Loss Code Snippet- noobj loss
- 负样本对应的grid计算noobj loss
- 负样本c为0
- BCEWithLogitsLoss(c_p, c_t)
- 负样本对应的grid计算noobj loss
- obj loss
- 正样本对应的grid计算obj loss
- 正样本c为1
- loss计算有两种策略
- 当做二分类问题, c_t使用原始值1
- 当做回归问题, 使用iou作为c_t
- 将prediction映射成与target等价的predict box
- pred xywh = sigmod(x,y), exp(w,h) x (anchor wh) <–> target xywh
- 将prediction映射成与target等价的predict box
- 正样本对应的grid计算obj loss
- box loss
- pred box与target的xywh做回归
- pred xywh = sigmod(x,y), wh <–> target xy, log((w,h) / (anchor wh))
- cls loss
- CrossEntropyLoss(cls, label)
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.